How Do API Plugins Work
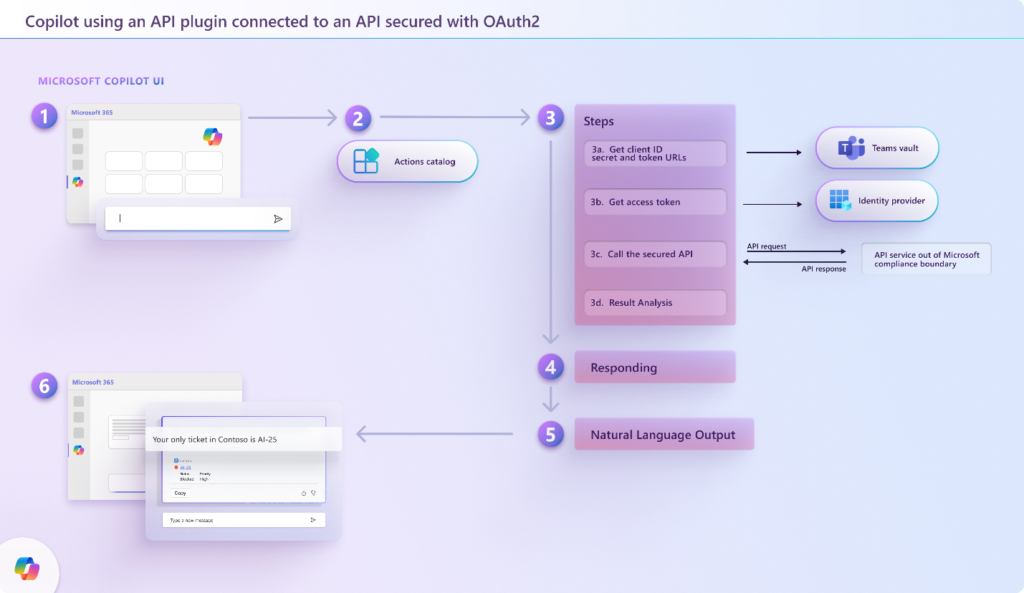
Declarative agents use API plugins to communicate with APIs in order to read and modify data. Each time a user submits a prompt (1), the declarative agent evaluates the prompt to check whether there are appropriate functions to invoke (2). If it finds a function that matches the user’s prompt, it authenticates if necessary (3a, 3b). Then, it builds the required API request, calls the API (3c), processes its response (3d), and constructs a reply for the user (6). The following diagram shows this process in more detail:
How Does the Agent Know Which Function to Invoke?
When you create an API plugin, you define its name, description, and one or more functions. For each function, you specify a description. The declarative agent uses all this information to determine which function it should invoke. Each time a user submits a prompt to your declarative agent, it uses its underlying language model to evaluate the prompt against the available descriptions of the plugin and its functions, in order to decide whether there is an appropriate function to invoke.
Once the agent selects a function to invoke, it maps that function to the operation in the API specification. Based on the API information, it builds the API request and processes the API response.
