Reporting and logging
When an unexpected event occurs—like a repository deletion or a failed workflow run—you need precise details: who did it, when, and how. GitHub’s audit logs capture this information for troubleshooting, compliance, and security investigations.
You can access the audit log through GitHub.com, GitHub Enterprise Server, or GitHub AE. Interacting with the audit log via either the GraphQL API or the REST API allows you to retrieve specific types of information, though there are some limitations.
Tip
Suppose a critical repository vanished overnight. You’ll use the audit logs to pinpoint the deletion event and restore continuity.
What are Log Records?
Your organization’s audit log records actions taken by organization members. Available to organization owners, the log provides information about actions that affect the organization, including:
- The repository in which the action was performed.
- The user who performed the action.
- The action that was performed.
- The country or region where the action took place.
- The action’s date and time.
Note
Logs are retained for up to 90 days in GitHub Enterprise Cloud (120 days via GraphQL on Enterprise Server).
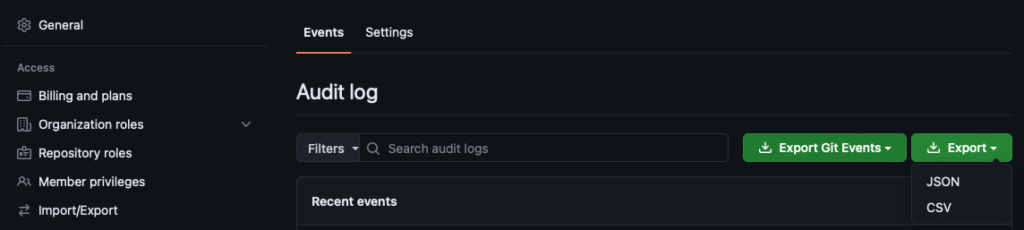
Viewing and exporting Audit Logs via the GitHub UI
- On GitHub.com, navigate to your organization’s Settings > Audit log.
- Use the Filters field to narrow results by qualifier (actor, repo, action, date).
- Click Export and choose CSV or JSON to download.
| Qualifier | Example value |
|---|---|
action | team.create |
actor | octocat |
user | codertocat |
org | octo-org |
repo | octo-org/documentation |
created | 2019-06-01 |
Accessing Audit Logs via API
REST API
- Scope: Enterprise Cloud (up to 90 days; Git events for 7 days).
- Monitors: Settings changes, permission updates, team membership, application changes, plus Git events (push, pull, merge).
GET /orgs/{org}/audit-log?phrase=git.push
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKENGraphQL API
- Scope: Enterprise Server (up to 120 days).
- Monitors: Settings changes, permission updates, team membership, application changes.
- Limitations: Does not include Git events (pushes, pulls).
query {
auditLogEntries(first: 20, query: "org:octo-org action:repo.cleanup") {
nodes {
action
actor { login }
createdAt
repository { name }
}
}
}Investigating missing assets
To recover or audit missing resources like repositories or teams:
- Identify the asset (e.g.,
repository.deleted). - Query the API with event filters:
- REST:
?phrase=repository.deleted - GraphQL:
query auditLogEntries(query: "repository.deleted")
- REST:
- Inspect metadata: actor, timestamp, repository/team name.
- Remediate: restore from backup or revisit permissions.
GET /orgs/{org}/audit-log?phrase=repository.deleted
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKENquery {
auditLogEntries(first: 10, query: "repository.deleted") {
nodes {
action
actor { login }
createdAt
}
}
}Use cases for Audit Logs
- Security incidents: Trace unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
- Compliance audits: Demonstrate policy enforcement (SOC 2, ISO 27001).
- Operational troubleshooting: Diagnose CI/CD failures or permission errors.
- Access monitoring: Review API token usage and SSH/Git activity.
Security and compliance
- Data Retention: 90 days on Enterprise Cloud; 120 days on Enterprise Server.
- Access Control: Only owners and security managers can view logs.
- IP Logging: Records source IP to detect suspicious access.
- Regional Compliance: Meets data-handling requirements.
Audit Log streaming
Stream logs in real time to SIEM platforms (Splunk, Datadog) for long-term storage:
- Go to Settings > Audit log.
- Under Streaming, configure a destination (AWS S3, Azure Event Hubs).
- Verify events arrive in your SIEM.
Additional Audit Log types
- Git Activity Log: Tracks pushes, pulls, merges (
phrase=git.push). - API Activity Log: Tracks REST/GraphQL requests (
phrase=api.request). - Enterprise Managed Users (EMU): Includes
user.login,repository.permissions_updated,repository.forked. - Token Usage: Filter by
phrase=tokento identify compromised credentials.
Key security features of a GitHub Repository
- SECURITY.md: Define reporting process and supported versions.
- Branch Protection: Enforce reviews, status checks, and commit signing.
- Dependabot Alerts: Automatic vulnerability detection and updates.
- Code Scanning: Continuous analysis via CodeQL.
- Secret Scanning & Push Protection: Real-time prevention and alerts.
- Security Advisories: Draft, collaborate, and publish advisories.
- Dependency Graph: Visualize and audit dependencies.
- 2FA & RBAC: Enforce strong authentication and least privilege.
API access and integrations
| Token Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Personal Access Tokens (PATs) | Tied to a user account; simple scripts; broad scope. |
| Installation Tokens | For GitHub Apps installations; fine-grained permissions. |
| OAuth Tokens | For OAuth apps; scoped access; requires least privilege. |
| Device Tokens | For device-based authentication flows. |
| Refresh Tokens | To renew expired tokens without re-authentication. |
| Rate Limit Type | Limit |
|---|---|
| Unauthenticated | 60 requests per hour. |
| Authenticated | 5,000 requests per hour. |
| Apps | Varies by installation. |
Check via API:
curl -H "Authorization: token YOUR_TOKEN" \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json" \
https://api.github.com/rate_limitGitHub Apps offer fine-grained permissions ideal for organizational integrations, while PATs suit basic scripts. OAuth Apps should be granted least privilege, with event subscriptions managed and reviewed regularly. Organizations can restrict untrusted apps through settings to enhance security. Enterprise Managed Users provide managed accounts with limited scope, ensuring compliance. Data residency policies help organizations store logs in specified regions, aligning with regulatory requirements.
