Setting security policies
In this unit, you’ll learn how to set up preventive measures, document vulnerabilities, leverage GitHub’s security tools (including enterprise-grade and compliance features), scrub sensitive data when needed, manage policies, and audit activity.
Imagine you’re an admin onboarding new collaborators: you want them in the right repos, reporting issues clearly, and following consistent standards. Let’s set your security policies.
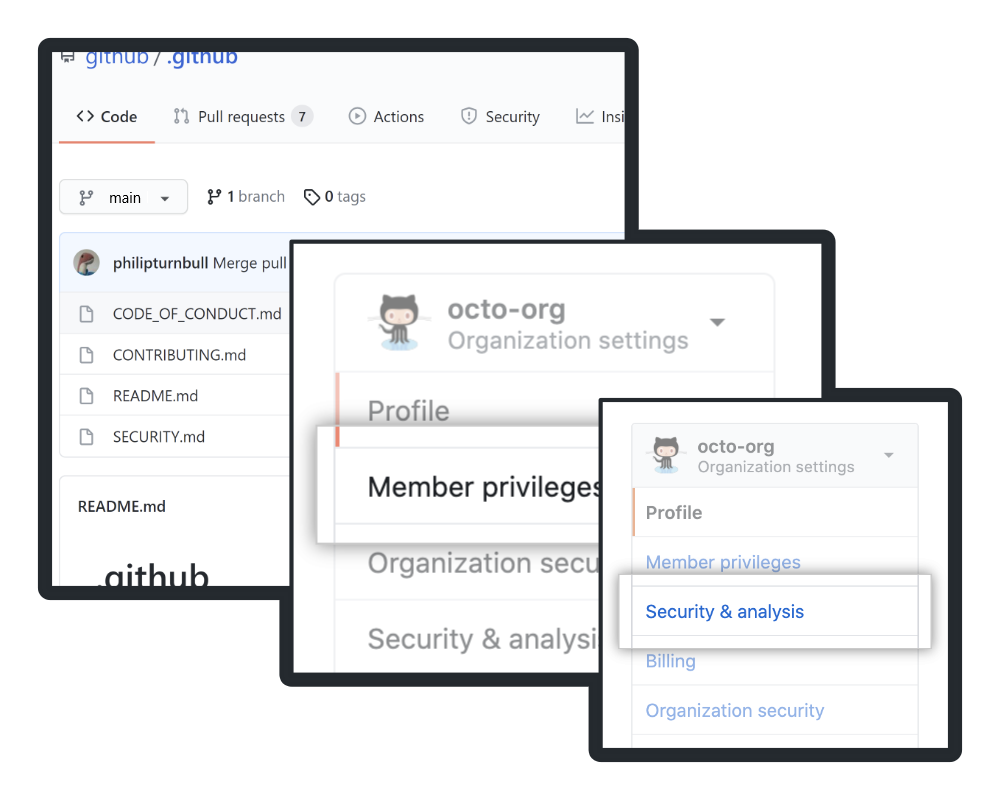
Why security policies matter
Security policies maintain your GitHub ecosystem’s integrity by:
- Guiding workflows: Secure, standardized processes
- Reporting clarity: Clear steps for vulnerability disclosure
- Access control: Least-privilege permissions to limit risk
Apply policies at the repo, org, or enterprise level—enterprise-wide rules enforce uniformity, while org-level settings let you tailor per project.
Documenting security
Clear docs are the first defense.
SECURITY.md
The SECURITY.md file tells users which versions you support, how to report issues, and any legal disclaimers or known risks.
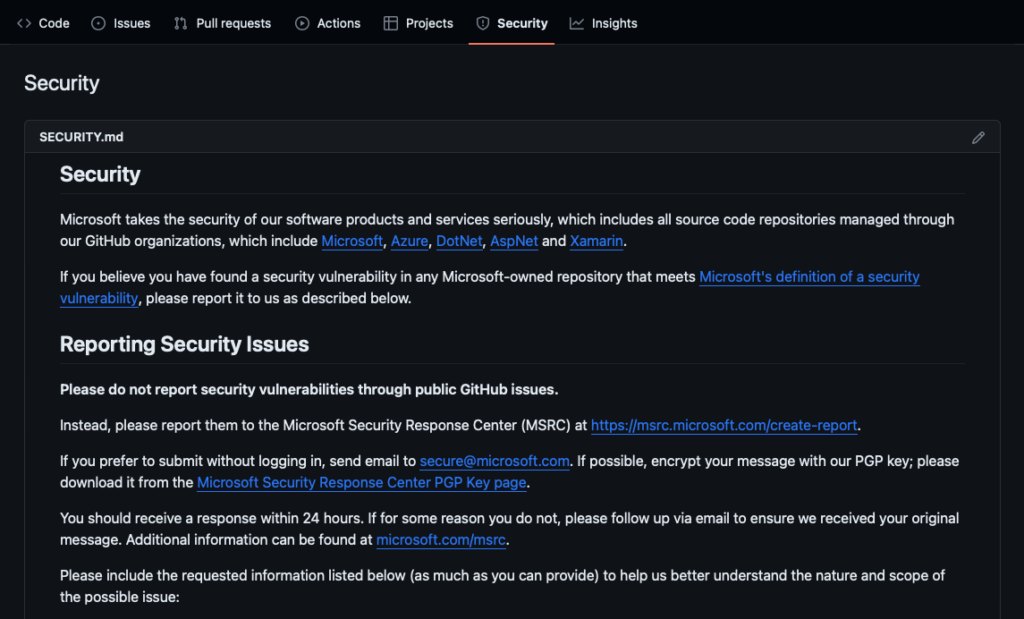
Other community health files
GitHub recognizes key community files that improve project transparency:
| File | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | Community behavior standards. |
| CONTRIBUTING.md | Contribution guidelines. |
| DISCUSSION category forms | Custom templates for community discussions. |
| FUNDING.yml | Displays sponsor options. |
| GOVERNANCE.md | Explains decision-making structure. |
| Issue/PR templates + config.yml | Standardizes contributor input. |
| README.md | Introduces and explains your project. |
| SUPPORT.md | Provides help resources. |
Security settings & enforcement
Choose trust vs. control based on team size: small teams might use broad permissions; large teams need stricter policies.
Configuration levels
- Org-level: Settings > Member privileges
- Enterprise-level: Your enterprises > Policies > Repository policies
Enterprise rules override org rules; org owners can’t change locked settings.
Note
Features and required interactions vary by repo type and license.
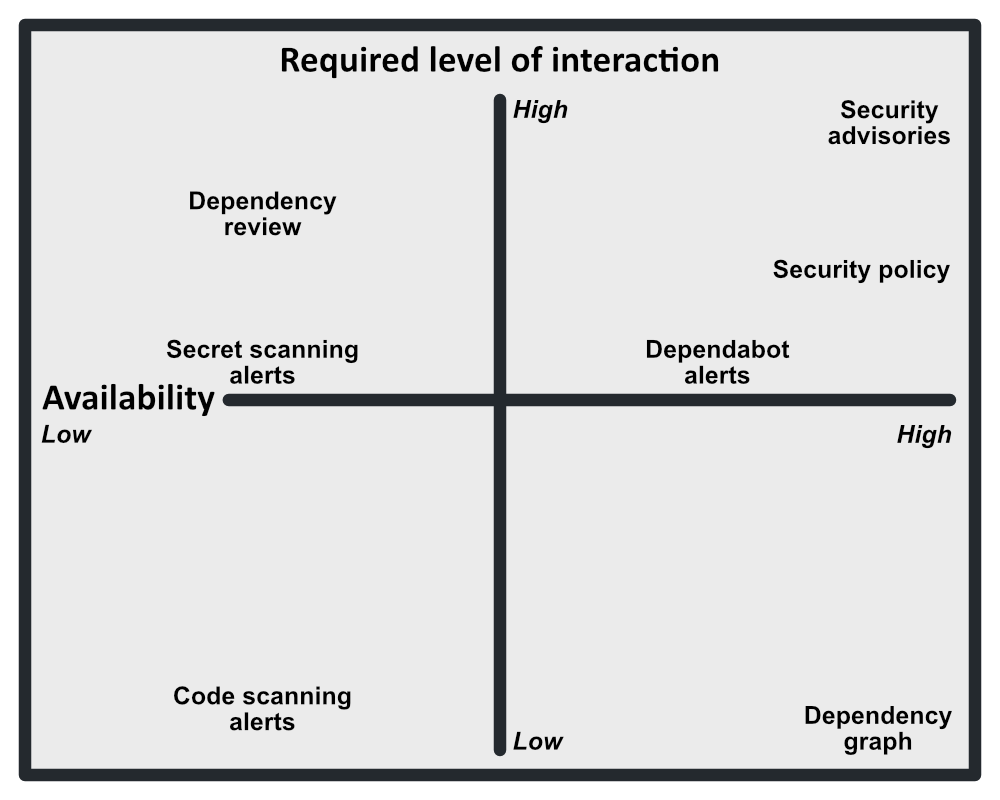
Available security tools
- All repos: Access controls, SECURITY.md, Dependabot alerts/updates, advisories
- With Advanced Security: Code scanning, secret scanning, dependency review
Enhancing enterprise security with GitHub
GitHub’s enterprise features bolster your security posture and compliance.
- Security Features
- GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS): Code scanning, secret scanning, dependency reviews
- Security Configurations: Enforce consistent settings across all repos
- Compliance Support
- Compliance reports: SOC 1 Type 2, SOC 2 Type 2, ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certifications available for audits and regulatory needs
Scrubbing sensitive data from GitHub repositories
When secrets leak, you must rewrite history or engage GitHub support.
Rewrite history
Legacy: git filter-branch to remove files:
git filter-branch --force --index-filter \
'git rm --cached --ignore-unmatch path/to/sensitive_file' \
--prune-empty --tag-name-filter cat -- --allRecommended: BFG Repo-Cleaner:
java -jar bfg.jar --delete-files path/to/sensitive_file.git
# or replace strings:
java -jar bfg.jar --replace-text passwords.txtClean up and force-push:
git reflog expire --expire=now --all
git gc --prune=now --aggressive
git push origin --force --allContact GitHub Support
For public repos, cached indexes may persist.
- (Optional) Delete the repo if data is critical.
- Rewrite history & force-push.
- Request removal via GitHub Support with repo name, commits/files, and confirmation of history rewrite to flush caches.
Prevent leaks:
- Use
.gitignore - Store secrets with GitHub Secrets or secret managers
- Scan regularly with GitGuardian or truffleHog
Publishing security advisories
When vulnerabilities arise, use GitHub security advisories to:
- Privately collaborate on fixes
- Clearly communicate details
- Document mitigation steps
A good advisory lists the affected versions, severity, patch status, and CVE references. Use GitHub’s built-in workflow to manage and publish advisories efficiently.
Enabling secure software development and ensuring compliance
Each policy is designed to balance security and usability, offering options that range from minimal restrictions to highly controlled environments. The table below provides an overview of various security policies categorized by their level of control.
| Control Level | Recommended Policies & Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Low Control (Guidance & Best Practices) | Security advisories & code scanning; Dependabot alerts; Branch protection rules (optional reviews) | Teams needing flexibility with best security practices |
| Moderate Control (Enforced Rules) | Required branch protection; Commit signing; Org-wide security policies; Monitoring webhooks | Teams needing governance with developer autonomy |
| High Control (Strict Compliance & Governance) | Enforce SAML SSO & 2FA; Restrict visibility & forking; Mandatory PR approvals; Prevent force pushes; CI/CD security checks | Organizations with strict compliance requirements (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001) |
Key security and compliance features in GitHub Enterprise
- Secure Code Development
- Code Scanning (GHAS): Automatically detect vulnerabilities via CodeQL.
- Secret Scanning: Prevent hardcoded secrets.
- Dependency Review & Dependabot: Identify and update vulnerable dependencies.
- Enforcing Compliance Policies
- Branch Protection Rules: Require PR reviews, status checks, and signed commits.
- Security Rulesets: Apply policies across multiple repos.
- Audit Logs & API Monitoring: Track activity and changes.
- Controlling Access & Authentication
- Enforce SAML SSO & 2FA: Strong authentication for all users.
- Restrict Repository Visibility: Control who can view, fork, or clone.
- Fine-Grained Access Control: Assign roles per team or project.
When to use different security and compliance profiles
- Startups & Agile Teams: Moderate control with branch protection, Dependabot, and secret scanning.
- Enterprises & Regulated Industries: High control with SAML SSO, audit logging, security rulesets, and strict repo controls.
- Open Source Projects: Low to moderate control with code scanning, dependency updates, and community guidance.
Defining Organization and Enterprise policies
Organization policies and enterprise policies set governance, access, and workflow rules to ensure security and compliance.
Key aspects
- Security & Access Control: SAML SSO, 2FA, RBAC, repo visibility.
- Compliance & Governance: Audit logging, branch protection, commit signing.
- Development Workflow & Automation: PR approvals, security rulesets, Actions policies.
- Code & Dependency Security: Code scanning, secret scanning, Dependabot, action restrictions.
Any enterprise-level policy in “Your enterprises > Policies > Repository policies” overrides org-level settings under Settings > Member privileges.
