What is GitHub?
In this unit, we will review the following learning objectives:
- General overview of the GitHub Enterprise platform
- How to create a repository
- Add files to a repository
- How to search for repositories
- Introduction to gists and wikis
GitHub
GitHub is a cloud platform that uses Git, a distributed version control system, as its foundation.
The GitHub platform simplifies project collaboration and provides a website, command-line tools, and an integrated workflow that enables developers and users to work together efficiently.
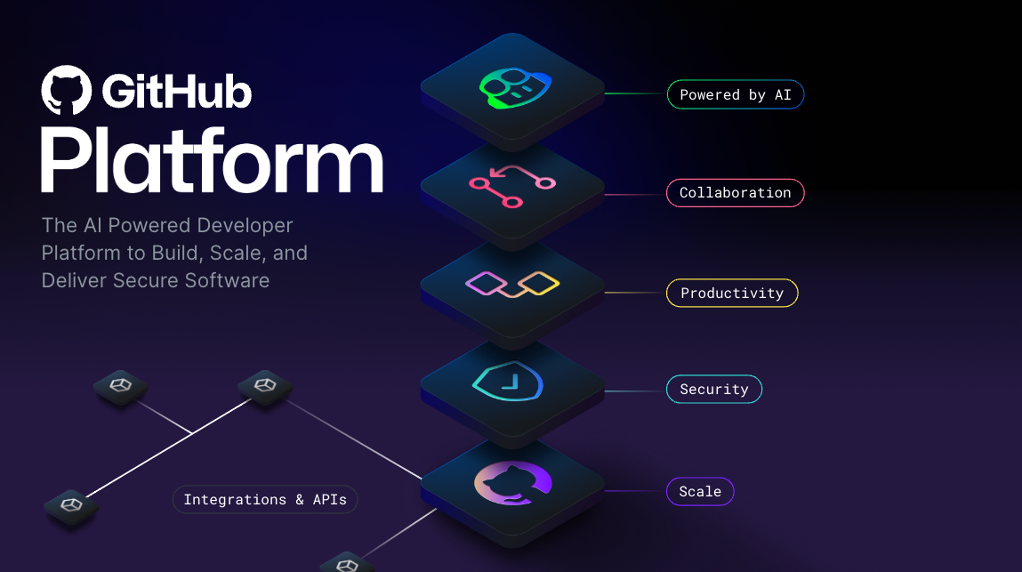
As we saw earlier, GitHub offers an AI-powered development platform to build, scale, and deliver secure software.
Now let’s look at the fundamental pillars of the GitHub Enterprise platform: AI, Collaboration, Productivity, Security, and Scalability.
🤖 AI
Generative AI is radically transforming software development.
The GitHub Enterprise platform enhances:
- Collaboration with AI-assisted pull requests and issues
- Productivity through Copilot
- Security by automating checks faster
🤝 Collaboration
Collaboration is at the heart of GitHub.
Inefficient collaboration leads to wasted time and money. GitHub solves this with a suite of streamlined tools:
- Repositories, Issues, Pull Requests, etc.
- Allowing developers, project managers, and operations leaders to work faster together, reduce approval times, and deliver more quickly
⚙️ Productivity
Productivity is boosted through automation built into the GitHub Enterprise platform:
- Integrated CI/CD tools
- Automated tasks
- Less manual administration
- More time for innovation
🔐 Security
GitHub integrates security from the start of development:
- Native security features
- Private code within your organization
- Security overview
- Dependabot integration
GitHub complies with global standards and is trusted by enterprises and regulated industries, including Microsoft.
🌍 Scalability
GitHub is the largest developer community in the world:
- Over 100 million developers
- Over 330 million repositories
- Millions of deployments
This scale enables GitHub to understand developers’ changing needs and adapt the platform accordingly.
🎯 In Summary
The GitHub Enterprise platform focuses on:
- Developer experience
- Effective collaboration
- Productivity tools
- Built-in security
- Powerful AI — all in a unified platform
📁 Introduction to Repositories
Key points review:
- What is a repository?
- How to create a repository
- Add files to a repository
- Search for repositories
- Introduction to gists, wikis, and GitHub Pages
📌 What is a Repository?
A repository contains all your project files and the revision history of each file.
It is essential for collaboration, managing your work, tracking changes, and working as a team.
🛠️ How to Create a Repository
You can create a repository on your personal account or in an organization where you have the necessary permissions.
From GitHub.com:
- In the upper-right corner of any page, click the dropdown menu
- Select “New repository”
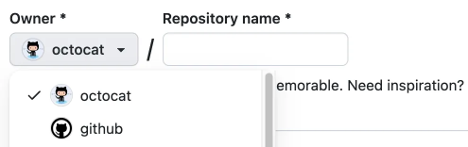
Use the Owner dropdown menu to select the account to which you want to assign ownership of the repository.
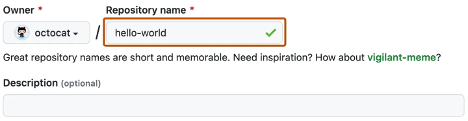
Type a name for your repository, along with an optional description.
Choose the repository visibility
- Public repositories are accessible to everyone on the Internet.
- Private repositories are accessible only to you, to people you explicitly share access with, and, for organization repositories, to certain organization members.
Select Create repository, and congratulations! 🎉 You’ve just created a repository!
Next, let’s see how to add files to your repository.
📁 How to Add a File to Your Repository
Files on GitHub can serve multiple purposes, but their main goal is to store data and information about your project.
👉 To add a file to a repository, you must have at least Write access to that repository.
Steps to add a file:
- On GitHub.com, go to the repository’s main page.
- In your repository, navigate to the folder where you want to create a file:
- Click Create new file, or
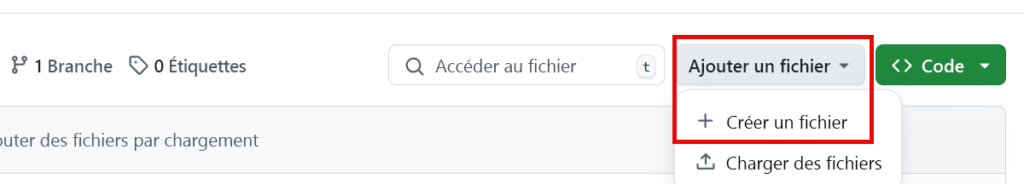
- Upload an existing file.
- Once in the correct folder, above the list of files, click the Add file dropdown menu ᐁ.
- Select Create new file.
In the Filename field, type the name and extension of the file.
To create subfolders, use the directory separator /.
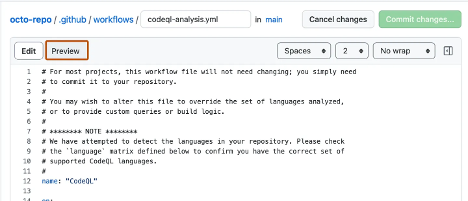
In the File content text area, enter the content of the file.
To preview the new content, above the text area, click Preview.
Select “Commit changes.”
In the Commit message field, enter a short and clear message describing the change made to the file.
You can attribute the commit to multiple authors by mentioning them in the message.
If you have multiple email addresses associated with your GitHub account, click the email address dropdown menu.
Then select the email address to use as the author’s address for the commit.
Only verified addresses appear in this menu.
If you have enabled email privacy, the default address will be:
[username]@users.noreply.github.com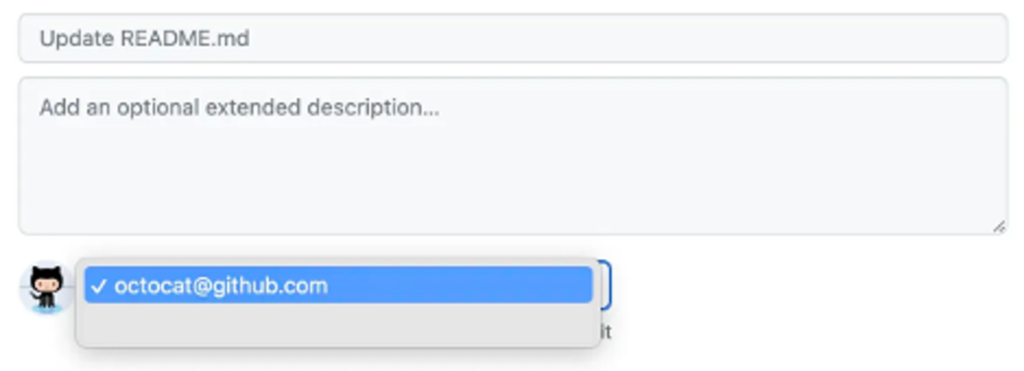
Select “Commit changes.”
In the Commit message field, enter a short and clear message describing the change made to the file.
You can attribute the commit to multiple authors by mentioning them in the message.
If you have multiple email addresses associated with your GitHub account, click the email address dropdown menu.
Then select the email address to use as the author’s address for the commit.
Only verified addresses appear in this menu.
If you have enabled email privacy, the default address will be:
[username]@users.noreply.github.com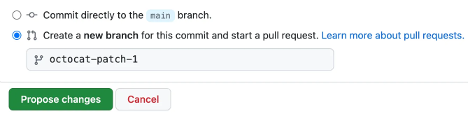
Select Validate changes or Suggest changes.
🎉 Congratulations, you’ve just created a new file in your repository!
You’ve also created a new branch and made a commit.
Before moving on to the next unit about branches and commits, let’s take a quick look at gists, wikis, and GitHub Pages, as they are similar to repositories.
📄 What is a gist?
Now that you understand repositories, let’s see what a gist is.
Like repositories, gists make it easy to share code snippets with others.
Each gist is a Git repository that you can fork, clone, and make public or secret.
Public gists are visible to everyone and can be viewed or searched.
Secret gists are not indexed, but they’re not completely private: anyone with the URL can access them.
👉 To learn more, check out the article Creating gists in the Resources section at the end of this module.
📚 What is a wiki?
Every repository on GitHub.com has a section dedicated to documentation called a wiki.
You can use your repository’s wiki to share detailed content about your project, such as:
- How to use it
- How it was designed
- Its core principles
While a README file gives a quick overview of your project, the wiki provides more comprehensive documentation.
🔒 If your repository is private, only people with at least read access will be able to view the wiki.
